Dr. Alexander Zarbock1,2
in cooperation with
PD Dr. Martin Wild1
Westphalian Wilhelm's University of Münster
1Max-Planck Institute for Molecular Biomedicine
Department of Vascular Cell Biology
Röntgenstrasse 20
48149 Münster
2Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine
Albert-Schweitzer-Str. 33
48149 Münster
| 
|
Email:
Net:
| zarbock@uni-muenster.de
www.mpi-muenster.mpg.de/nvz/vz.shtml |
The
research group of Dr. Alexander Zarbock is interested in understanding
the molecular mechanisms of leukocyte recruitment into inflamed tissue.
Glycosylation of
adhesion molecules participating in leukocyte recruitment is of particular importance.
Leukocyte
recruitment into inflamed tissue is tightly regulated. Reduced
neutrophil recruitment can result in a diminished ability to fight
invading microorganisms. During inflammation, leukocytes roll along the
endothelial wall and integrate inflammatory signals. Leukocyte
activation by carbohydrate-binding selectins and by chemokines
regulates integrin adhesiveness. Binding of activated integrins to
their counter-receptors on endothelial cells induces leukocyte arrest
and firm adhesion. Adherent neutrophils can be further activated to
undergo crawling, transmigration and respiratory burst.
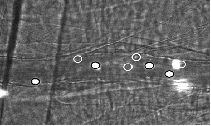 |
Intravital
microscopy of the cremaster muscle of mixed chimeric mice 6 weeks after
bone marrow transplantation. Neutrophils from LysM-GFP+ mice (black circle) and gene-deficient mice (GFP- cells, white circle).
|
The
first step of this cascade (‘capturing’) is mediated by selectins
expressed on endothelial cells and the main counter-receptor,
P-selectin glycoprotein ligand (PSGL)-1, on leukocytes. PSGL-1 can bind
all selectins (P-, E-, and L-selectin). For optimal selectin binding,
PSGL-1 must undergo post-translational modifications. Several
glycosyltransferases
are involved in this process including core 2
N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase, α1-3 fucosyltransferases FucT-VII and
FucT-IV, β1-4 galactosyltransferase-1, and α2-3 sialyltransferase
ST3GalIV. Studies with mice lacking one or multiple of these
glycosyltransferases demonstrated a broad array of leukocyte rolling
defects ranging from a mild capturing defect to an almost complete loss
of leukocyte rolling. In addition to these modifications, sulfation of
tyrosines near the N-terminus of PSGL-1 by distinct
tyrosylsulfotransferases contributes to the enhanced P-selectin binding
to PSGL-1. Binding of selectins to their counter-receptors not only
mediates capturing but also activates different signaling pathways.
Understanding the different signaling pathways and how they interact
may facilitate the development of therapeutics that only modulate the
desired function.
Our work is supported by a strong interdisciplinary and international network.





