New Insights into the Homogeneity of Interphases
Interphases influence the lifetime of lithium-ion battery cells (LIB) enormously. Understanding their composition, thickness and homogeneity is essential. A team of MEET Battery Research Center led by Bastian Heidrich has therefore investigated how homogeneous the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) and the cathode electrolyte interphase (CEI) are between the negative or positive electrode and the electrolyte. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements have shown that the thickness of the organic part of the SEI varies.
Standardised Measurement Methodology for Better Reproducibility
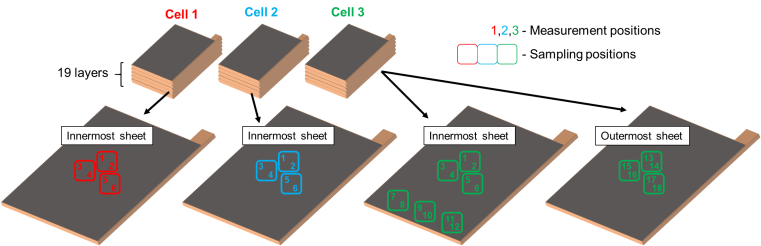
The interphases of multi-layered pouch cells were examined at several, different positions on multiple electrode sheets per cell. “We took a total of 106 measurements – an enormous number in battery research,” says MEET scientist Bastian Heidrich. With the result that both interphases are very homogeneous locally – in a radius of about one square centimetre. If the radius is extended to about five square centimetres on the same sample, the SEI thicknesses differ significantly. “By analysing the organic and inorganic SEI components separately, we have shown that the thickness of the organic part of the SEI can vary significantly. Comparing results of samples with different SEI thickness, could lead to fatal misinterpretation. A varying SEI thickness does not mean that the composition of the interphase itself is inhomogeneous, although XPS results of such samples will have high standard deviation and thus imply this,” says Heidrich.
XPS measurements have been established in battery research since the 1980s. “With our investigations, we are now showing what influence standard deviations can have on the interpretation of measurement results,” explains Heidrich. “Researchers often try to achieve the lowest possible standard deviations so that results have a supposed significance. But if a certain standard deviation is intrinsic to a particular system, we can also draw conclusion about the nature of our samples from this data.” A standardised measurement methodology and interpretation helps to compare the results of established systems with those of future systems in order to identify approaches for further research and development.
Original Publication Provides Further Insights into the Research
The MEET researchers Bastian Heidrich, Dr Markus Börner, Dr Philip Niehoff and Prof. Dr Martin Winter have published the detailed results of their research as an open access article in the scientific journal “Journal of Energy Storage”.

