Subprojects
Stochastic Structure Modeling (Ulm Univeristy)
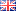
 On the basis of experimental 3D imaging data, new and aged electrode morphologies are
represented by a realistic (stochastic) 3D structure model. To this end, structurally segmented 3D
data of different imaging techniques is merged and statistically classified. Degradation effects
including emerging phases (e.g. Li-plating) are integrated for aged electrodes, enabling the
validation of the mathematical-physical modeling implemented by the project partners.
(more ...)
On the basis of experimental 3D imaging data, new and aged electrode morphologies are
represented by a realistic (stochastic) 3D structure model. To this end, structurally segmented 3D
data of different imaging techniques is merged and statistically classified. Degradation effects
including emerging phases (e.g. Li-plating) are integrated for aged electrodes, enabling the
validation of the mathematical-physical modeling implemented by the project partners.
(more ...)
Continuum Modeling (DLR at Helmholtz Institute Ulm)
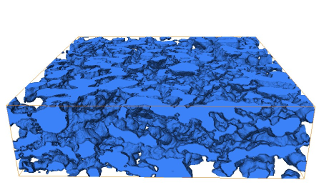
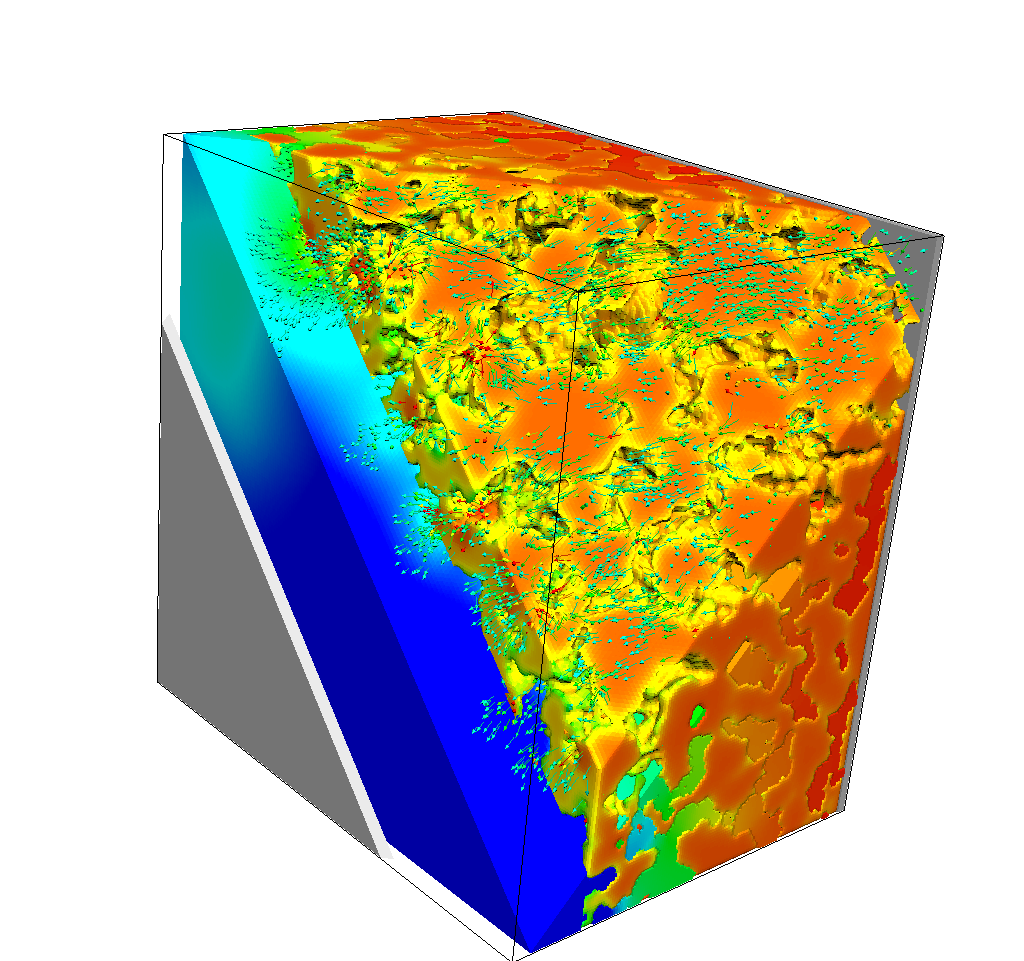 In this subproject, partial differential equation models for the description of the transport and electrochemical
reaction kinetics in a multi-phase multiscale microstructure of a lithium-ion battery cell are developed.
The modeling is based on an established transport model for a conventional three-phase lithium-ion battery,
consisting of the active particles of the anode and cathode as well as a liquid electrolyte.
The focus is on the inclusion of additional minority phases, which are of great importance for the
functionality of the battery.
We are concentrating on an additional metallic lithium phase in the anode, which is produced by one of
the most important degradation phenomena, lithium plating.
(more ...)
In this subproject, partial differential equation models for the description of the transport and electrochemical
reaction kinetics in a multi-phase multiscale microstructure of a lithium-ion battery cell are developed.
The modeling is based on an established transport model for a conventional three-phase lithium-ion battery,
consisting of the active particles of the anode and cathode as well as a liquid electrolyte.
The focus is on the inclusion of additional minority phases, which are of great importance for the
functionality of the battery.
We are concentrating on an additional metallic lithium phase in the anode, which is produced by one of
the most important degradation phenomena, lithium plating.
(more ...)
Multiscale Numerics (Fraunhofer ITWM)
The aim is the development of numerical algorithms for the battery models developed in MULTIBAT, which are solved on the networked geometries also created in this project. Part of the work is the extension of the algorithms currently implemented in the BEST battery simulation software from two-phase to multi-phase materials. To this end, existing algorithms for static geometries in BEST are used as a basis for the development of algorithms with a temporal change in the geometry. To speed up the computation, multiscale finite element and multiscale finite volume methods are developed for the given models.
Model Order Reduction (University of Münster)
 Goal of this subproject is the development, numerical analysis, implementation and validation of
efficient model order reduction methods for the simulation of two- and three-phase multiscale problems
on static micro-geometries, as well as the application of these methods for the simulation of
degradation processes in lithium-ion batteries. In addition to the method development, we are interested
in a posteriori error analysis and the use of the resulting error estimators for the construction
of the reduced approximating spaces. Another focus lies on the implementation and validation of the developed
model reduction approach.
Goal of this subproject is the development, numerical analysis, implementation and validation of
efficient model order reduction methods for the simulation of two- and three-phase multiscale problems
on static micro-geometries, as well as the application of these methods for the simulation of
degradation processes in lithium-ion batteries. In addition to the method development, we are interested
in a posteriori error analysis and the use of the resulting error estimators for the construction
of the reduced approximating spaces. Another focus lies on the implementation and validation of the developed
model reduction approach.
Algorithm Integration, Software Interfaces and Validation
(Fraunhofer ITWM)
In this subproject, the different-scale and different-dimensional mathematical algorithms and models developed within the project are integrated into a mathematical simulation method for the degradation prediction of lithium-ion batteries. For example, the already existing interfaces for traditional reduced basis methods developed at the University of Münster are extended and integrated with the battery simulation software BEST and the CoRheoS platform developed at ITWM in order to make the numerical models developed in MULTIBAT available for model order reduction.