|
rbmatlab 0.10.01
|
|
rbmatlab 0.10.01
|
RBmatlab is a MATLAB© library providing routines for the solution of numerical schemes based on partial differential equations. The library consists of three main modules:
Note, that these three modules depend on each other in the following way:
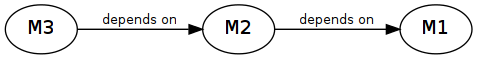
As a consequence, if you want to implement your own reduced basis procedure with RBmatlab, you need to make yourself familiar with all three modules. Of course, it makes sense to use the first module for discretization methods of partial differential equations independently, as it provides many useful tools for the implementation of your favourite numerical scheme.
Users new to RBmatlab should first get a copy of the RBmatlab-HowTo describing a high-level usage of a simple reduced basis problem with RBmatlab. In order to learn more about the concepts, we suggest to follow the order of the above list and to understand each of the basic demos
Furthermore, there is a directory with regression tests which could also be helpful.
In order to implement a full reduced model, the four main interface classes IDetailedModel, IDetailedData, IReducedData and IReducedModel need to be specified. More general information on these interface classes can be found in Section Interface classes.
The suggested course of action for a reduced basis scheme is to
The reduced basis generation algorithms can also make use of detailed simulations from other software packages, if those stick to the interface of the RBmatlab framework. An example is the Dune module dune-rb for which a model implementation exists here.
This documentation is generated by Doxygen - an automatic documentation tool. Although designed for C-like languages, Doxygen allows to pre-process the source code by a filter programm that makes Matlab-code parseable by Doxygen as well. In order to extend and re-build this documentation by your own, you therefore
make_docu.sh in the base directory of your RBmatlab installation.Note, that an easy access to the HTML-documentation from the Matlab© prompt, is provided by htdoc().
 1.7.4
1.7.4