pymor.algorithms package¶
Submodules¶
adaptivegreedy module¶
-
class
pymor.algorithms.adaptivegreedy.AdaptiveSampleSet(parameter_space)[source]¶ Bases:
pymor.core.interfaces.BasicInterfaceAn adaptive parameter sample set.
Used by
adaptive_greedy.Methods
AdaptiveSampleSetmap_vertex_to_mu,refine,visualizeBasicInterfacedisable_logging,enable_logging,has_interface_name,implementor_names,implementorsAttributes
AdaptiveSampleSetElementBasicInterfacelogger,logging_disabled,name,uid
-
pymor.algorithms.adaptivegreedy._estimate(mu, rd=None, d=None, reductor=None, error_norm=None)[source]¶ Called by
adaptive_greedy.
-
pymor.algorithms.adaptivegreedy.adaptive_greedy(discretization, reductor, parameter_space=None, use_estimator=True, error_norm=None, target_error=None, max_extensions=None, validation_mus=0, rho=1.1, gamma=0.2, theta=0.0, extension_params=None, visualize=False, visualize_vertex_size=80, pool=<pymor.parallel.dummy.DummyPool object>)[source]¶ Greedy basis generation algorithm with adaptively refined training set.
This method extends pyMOR’s default
greedygreedy basis generation algorithm by adaptive refinement of the parameter training set according to [HDO11] to prevent overfitting of the reduced basis to the training set. This is achieved by estimating the reduction error on an additional validation set of parameters. If the ratio between the estimated errors on the validation set and the validation set is larger thanrho, the training set is refined using standard grid refinement techniques.[HDO11] Haasdonk, B.; Dihlmann, M. & Ohlberger, M., A training set and multiple bases generation approach for parameterized model reduction based on adaptive grids in parameter space, Math. Comput. Model. Dyn. Syst., 2011, 17, 423-442 Parameters
- discretization
- See
greedy. - reductor
- See
greedy. - parameter_space
- The
ParameterSpacefor which to compute the reduced model. IfNone, the parameter space of thediscretizationis used. - use_estimator
- See
greedy. - error_norm
- See
greedy. - target_error
- See
greedy. - max_extensions
- See
greedy. - validation_mus
- One of the following:
- a list of
Parametersto use as validation set, - a positive number indicating the number of random parameters to use as validation set,
- a non-positive number, indicating the negative number of random parameters to use as validation set in addition to the centers of the elements of the adaptive training set.
- a list of
- rho
- Maximum allowed ratio between maximum estimated error on validation set vs. maximum estimated error on training set. If the ratio is larger, the training set is refined.
- gamma
- Weight of the age penalty term in the training set refinement indicators.
- theta
- Ratio of training set elements to select for refinement. (One element is always refined.)
- extension_params
- See
greedy. - visualize
- If
True, visualize the refinement indicators. (Only available for 2 and 3 dimensional parameter spaces.) - visualize_vertex_size
- Size of the vertices in the visualization.
- pool
- See
greedy.
Returns
Dict with the following fields
reduced_discretization: The reduced Discretizationobtained for the computed basis.extensions: Number of greedy iterations. max_errs: Sequence of maximum errors during the greedy run. max_err_mus: The parameters corresponding to max_errs.max_val_errs: Sequence of maximum errors on the validation set. max_val_err_mus: The parameters corresponding to max_val_errs.refinements: Number of refinements made in each extension step. training_set_sizes: The final size of the training set in each extension step. time: Duration of the algorithm. reduction_data: Reduction data returned by the last reductor call.
basic module¶
Module containing some basic but generic linear algebra algorithms.
-
pymor.algorithms.basic.almost_equal(U, V, product=None, norm=None, rtol=1e-14, atol=1e-14)[source]¶ Compare U and V for almost equality.
The vectors of
UandVare compared in pairs for almost equality. Two vectorsuandvare considered almost equal iff||u - v|| <= atol + ||v|| * rtol.The norm to be used can be specified via the
normorproductparameter.If the length of
Uresp.Vis 1, the single specified vector is compared to all vectors of the other array. Otherwise, the lengths of both indexed arrays have to agree.Parameters
- U, V
VectorArraysto be compared.- product
- If specified, use this inner product
Operatorto compute the norm.productandnormare mutually exclusive. - norm
- If specified, must be a callable, which is used to compute the norm
or, alternatively, one of the string ‘l1’, ‘l2’, ‘sup’, in which case the
respective
VectorArraynorm methods are used.productandnormare mutually exclusive. If neither is specified,norm='l2'is assumed. - rtol
- The relative tolerance.
- atol
- The absolute tolerance.
Defaults
rtol, atol (see
pymor.core.defaults)
ei module¶
This module contains algorithms for the empirical interpolation of Operators.
The main work for generating the necessary interpolation data is handled by
the ei_greedy method. The objects returned by this method can be used
to instantiate an EmpiricalInterpolatedOperator.
As a convenience, the interpolate_operators method allows to perform
the empirical interpolation of the Operators of a given discretization with
a single function call.
-
pymor.algorithms.ei.deim(U, modes=None, error_norm=None, product=None)[source]¶ Generate data for empirical interpolation using DEIM algorithm.
Given a
VectorArrayU, this method generates a collateral basis and interpolation DOFs for empirical interpolation of the vectors contained inU. The returned objects can be used to instantiate anEmpiricalInterpolatedOperator(withtriangular=False).The collateral basis is determined by the first
podmodes ofU.Parameters
- U
- A
VectorArrayof vectors to interpolate. - modes
- Dimension of the collateral basis i.e. number of POD modes of the vectors in
U. - error_norm
- Norm w.r.t. which to calculate the interpolation error. If
None, the Euclidean norm is used. - product
- Inner product
Operatorused for the POD.
Returns
- interpolation_dofs
NumPy arrayof the DOFs at which the vectors are interpolated.- collateral_basis
VectorArraycontaining the generated collateral basis.- data
Dict containing the following fields:
errors: Sequence of maximum approximation errors during greedy search.
-
pymor.algorithms.ei.ei_greedy(U, error_norm=None, atol=None, rtol=None, max_interpolation_dofs=None, copy=True, pool=<pymor.parallel.dummy.DummyPool object>)[source]¶ Generate data for empirical interpolation using EI-Greedy algorithm.
Given a
VectorArrayU, this method generates a collateral basis and interpolation DOFs for empirical interpolation of the vectors contained inU. The returned objects can be used to instantiate anEmpiricalInterpolatedOperator(withtriangular=True).The interpolation data is generated by a greedy search algorithm, where in each loop iteration the worst approximated vector in
Uis added to the collateral basis.Parameters
- U
- A
VectorArrayof vectors to interpolate. - error_norm
- Norm w.r.t. which to calculate the interpolation error. If
None, the Euclidean norm is used. - atol
- Stop the greedy search if the largest approximation error is below this threshold.
- rtol
- Stop the greedy search if the largest relative approximation error is below this threshold.
- max_interpolation_dofs
- Stop the greedy search if the number of interpolation DOF (= dimension of the collateral basis) reaches this value.
- copy
- If
False,Uwill be modified during executing of the algorithm. - pool
- If not
None, theWorkerPoolto use for parallelization.
Returns
- interpolation_dofs
NumPy arrayof the DOFs at which the vectors are evaluated.- collateral_basis
VectorArraycontaining the generated collateral basis.- data
Dict containing the following fields:
errors: Sequence of maximum approximation errors during greedy search. triangularity_errors: Sequence of maximum absolute values of interoplation matrix coefficients in the upper triangle (should be near zero).
-
pymor.algorithms.ei.interpolate_operators(discretization, operator_names, parameter_sample, error_norm=None, atol=None, rtol=None, max_interpolation_dofs=None, pool=<pymor.parallel.dummy.DummyPool object>)[source]¶ Empirical operator interpolation using the EI-Greedy algorithm.
This is a convenience method to facilitate the use of
ei_greedy. Given aDiscretization, names ofOperators, and a sample ofParameters, first the operators are evaluated on the solution snapshots of the discretization for the provided parameters. These evaluations are then used as input forei_greedy. Finally the resulting interpolation data is used to createEmpiricalInterpolatedOperatorsand a new discretization with the interpolated operators is returned.Note that this implementation creates one common collateral basis for all specified operators, which might not be what you want.
Parameters
- discretization
- The
DiscretizationwhoseOperatorswill be interpolated. - operator_names
- List of keys in the
operatorsdict of the discretization. The correspondingOperatorswill be interpolated. - parameter_sample
- A list of
Parametersfor which solution snapshots are calculated. - error_norm
- See
ei_greedy. - atol
- See
ei_greedy. - rtol
- See
ei_greedy. - max_interpolation_dofs
- See
ei_greedy. - pool
- If not
None, theWorkerPoolto use for parallelization.
Returns
- ei_discretization
DiscretizationwithOperatorsgiven byoperator_namesreplaced byEmpiricalInterpolatedOperators.- data
Dict containing the following fields:
dofs: NumPy arrayof the DOFs at which theOperatorshave to be evaluated.basis: VectorArraycontaining the generated collateral basis.errors: Sequence of maximum approximation errors during greedy search. triangularity_errors: Sequence of maximum absolute values of interoplation matrix coefficients in the upper triangle (should be near zero).
error module¶
-
pymor.algorithms.error.reduction_error_analysis(reduced_discretization, discretization=None, reductor=None, test_mus=10, basis_sizes=0, random_seed=None, estimator=True, condition=False, error_norms=(), error_norm_names=None, estimator_norm_index=0, custom=(), plot=False, plot_custom_logarithmic=True, pool=<pymor.parallel.dummy.DummyPool object>)[source]¶ Analyze the model reduction error.
The maximum model reduction error is estimated by solving the reduced
Discretizationfor given randomParameters.Parameters
- reduced_discretization
- The reduced
Discretization. - discretization
- The high-dimensional
Discretization. Must be specified iferror_normsare given. - reductor
- The reductor which has created
reduced_discretization. Must be specified iferror_normsare given. - test_mus
- Either a list of
Parametersto compute the errors for, or the number of parameters which are sampled randomly fromparameter_space(if given) orreduced_discretization.parameter_space. - basis_sizes
- Either a list of reduced basis dimensions to consider, or
the number of dimensions (which are then selected equidistantly,
always including the maximum reduced space dimension).
The dimensions are input for
~pymor.reductors.basic.reduce_to_subbasisto quickly obtain smaller reducedDiscretizationsfromrb_discretization. - random_seed
- If
test_musis a number, use this value as random seed for drawing theParameters. - estimator
- If
Trueevaluate the error estimator ofreduced_discretizationon the testParameters. - condition
- If
True, compute the condition of the reduced system matrix for the given testParameters(can only be specified ifrb_discretizationis an instance ofStationaryDiscretizationandrb_discretization.operatoris linear). - error_norms
- List of norms in which to compute the model reduction error.
- error_norm_names
- Names of the norms given by
error_norms. IfNone, thenameattributes of the given norms are used. - estimator_norm_index
- When
estimatorisTrueanderror_normsare specified, this is the index of the norm inerror_normsw.r.t. which to compute the effectivity of the estimator. - custom
List of custom functions which are evaluated for each test
Parameterand basis size. The functions must have the signaturedef custom_value(reduced_discretization, discretization=d, reductor, mu, dim): pass
- plot
- If
True, generate a plot of the computed quantities w.r.t. the basis size. - plot_custom_logarithmic
- If
True, use a logarithmic y-axis to plot the computed custom values. - pool
- If not
None, theWorkerPoolto use for parallelization.
Returns
Dict with the following fields
mus: The test Parameterswhich have been considered.basis_sizes: The reduced basis dimensions which have been considered. norms: NumPy arrayof the norms of the high-dimensional solutions w.r.t. all given testParameters, reduced basis dimensions and norms inerror_norms. (Only present whenerror_normshas been specified.)max_norms: Maxima of normsover the given testParameters.max_norm_mus: Parameterscorresponding tomax_norms.errors: NumPy arrayof the norms of the model reduction errors w.r.t. all given testParameters, reduced basis dimensions and norms inerror_norms. (Only present whenerror_normshas been specified.)max_errors: Maxima of errorsover the given testParameters.max_error_mus: Parameterscorresponding tomax_errors.rel_errors: errorsdivided bynorms. (Only present whenerror_normshas been specified.)max_rel_errors: Maxima of rel_errorsover the given testParameters.max_rel_error_mus: Parameterscorresponding tomax_rel_errors.error_norm_names: Names of the given error_norms. (Only present whenerror_normshas been specified.)estimates: NumPy arrayof the model reduction error estimates w.r.t. all given testParametersand reduced basis dimensions. (Only present whenestimatorisTrue.)max_estimate: Maxima of estimatesover the given testParameters.max_estimate_mus: Parameterscorresponding tomax_estimates.effectivities: errorsdivided byestimates. (Only present whenestimatorisTrueanderror_normshas been specified.)min_effectivities: Minima of effectivitiesover the given testParameters.min_effectivity_mus: Parameterscorresponding tomin_effectivities.max_effectivities: Maxima of effectivitiesover the given testParameters.max_effectivity_mus: Parameterscorresponding tomax_effectivities.errors: NumPy arrayof the reduced system matrix conditions w.r.t. all given testParametersand reduced basis dimensions. (Only present whenconditionsisTrue.)max_conditions: Maxima of conditionsover the given testParameters.max_condition_mus: Parameterscorresponding tomax_conditions.custom_values: NumPy arrayof custom function evaluations w.r.t. all given testParameters, reduced basis dimensions and functions incustom. (Only present whencustomhas been specified.)max_custom_values: Maxima of custom_valuesover the given testParameters.max_custom_values_mus: Parameterscorresponding tomax_custom_values.time: Time (in seconds) needed for the error analysis. summary: String containing a summary of all computed quantities for the largest (last) considered basis size. figure: The figure containing the generated plots. (Only present when plotisTrue.)
genericsolvers module¶
This module contains some iterative linear solvers which only use the Operator interface
-
pymor.algorithms.genericsolvers.apply_inverse(op, rhs, options=None, least_squares=False, check_finite=True, default_solver='generic_lgmres', default_least_squares_solver='generic_least_squares_lsmr')[source]¶ Solve linear equation system.
Applies the inverse of
opto the vectors inrhsusing a generic iterative solver.Parameters
- op
- The linear, non-parametric
Operatorto invert. - rhs
VectorArrayof right-hand sides for the equation system.- options
- The
solver_optionsto use (seesolver_options). - check_finite
- Test if solution only containes finite values.
- default_solver
- Default solver to use (generic_lgmres, generic_least_squares_lsmr, generic_least_squares_lsqr).
- default_least_squares_solver
- Default solver to use for least squares problems (generic_least_squares_lsmr, generic_least_squares_lsqr).
Returns
VectorArrayof the solution vectors.Defaults
check_finite, default_solver, default_least_squares_solver (see
pymor.core.defaults)
-
pymor.algorithms.genericsolvers.lgmres(A, b, x0=None, tol=1e-05, maxiter=1000, M=None, callback=None, inner_m=30, outer_k=3, outer_v=None, store_outer_Av=True)[source]¶
-
pymor.algorithms.genericsolvers.lsmr(A, b, damp=0.0, atol=1e-06, btol=1e-06, conlim=100000000.0, maxiter=None, show=False)[source]¶
-
pymor.algorithms.genericsolvers.lsqr(A, b, damp=0.0, atol=1e-08, btol=1e-08, conlim=100000000.0, iter_lim=None, show=False)[source]¶
-
pymor.algorithms.genericsolvers.solver_options(lgmres_tol=1e-05, lgmres_maxiter=1000, lgmres_inner_m=39, lgmres_outer_k=3, least_squares_lsmr_damp=0.0, least_squares_lsmr_atol=1e-06, least_squares_lsmr_btol=1e-06, least_squares_lsmr_conlim=100000000.0, least_squares_lsmr_maxiter=None, least_squares_lsmr_show=False, least_squares_lsqr_damp=0.0, least_squares_lsqr_atol=1e-06, least_squares_lsqr_btol=1e-06, least_squares_lsqr_conlim=100000000.0, least_squares_lsqr_iter_lim=None, least_squares_lsqr_show=False)[source]¶ Returns available solvers with default
solver_options.Parameters
- lgmres_tol
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lgmres. - lgmres_maxiter
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lgmres. - lgmres_inner_m
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lgmres. - lgmres_outer_k
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lgmres. - least_squares_lsmr_damp
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lsmr. - least_squares_lsmr_atol
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lsmr. - least_squares_lsmr_btol
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lsmr. - least_squares_lsmr_conlim
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lsmr. - least_squares_lsmr_maxiter
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lsmr. - least_squares_lsmr_show
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lsmr. - least_squares_lsqr_damp
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lsqr. - least_squares_lsqr_atol
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lsqr. - least_squares_lsqr_btol
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lsqr. - least_squares_lsqr_conlim
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lsqr. - least_squares_lsqr_iter_lim
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lsqr. - least_squares_lsqr_show
- See
scipy.sparse.linalg.lsqr.
Returns
A dict of available solvers with default
solver_options.Defaults
lgmres_tol, lgmres_maxiter, lgmres_inner_m, lgmres_outer_k, least_squares_lsmr_damp, least_squares_lsmr_atol, least_squares_lsmr_btol, least_squares_lsmr_conlim, least_squares_lsmr_maxiter, least_squares_lsmr_show, least_squares_lsqr_atol, least_squares_lsqr_btol, least_squares_lsqr_conlim, least_squares_lsqr_iter_lim, least_squares_lsqr_show (see
pymor.core.defaults)
gram_schmidt module¶
-
pymor.algorithms.gram_schmidt.gram_schmidt(A, product=None, atol=1e-13, rtol=1e-13, offset=0, find_duplicates=True, reiterate=True, reiteration_threshold=0.1, check=True, check_tol=0.001, copy=True)[source]¶ Orthonormalize a
VectorArrayusing the stabilized Gram-Schmidt algorithm.Parameters
- A
- The
VectorArraywhich is to be orthonormalized. - product
- The inner product
Operatorw.r.t. which to orthonormalize. IfNone, the Euclidean product is used. - atol
- Vectors of norm smaller than
atolare removed from the array. - rtol
- Relative tolerance used to detect linear dependent vectors (which are then removed from the array).
- offset
- Assume that the first
offsetvectors are already orthonormal and start the algorithm at theoffset + 1-th vector. - reiterate
- If
True, orthonormalize again if the norm of the orthogonalized vector is much smaller than the norm of the original vector. - reiteration_threshold
- If
reiterateisTrue, re-orthonormalize if the ratio between the norms of the orthogonalized vector and the original vector is smaller than this value. - check
- If
True, check if the resultingVectorArrayis really orthonormal. - check_tol
- Tolerance for the check.
- copy
- If
True, create a copy ofAinstead of modifyingAin-place. - find_duplicates
- unused
Returns
The orthonormalized
VectorArray.Defaults
atol, rtol, reiterate, reiteration_threshold, check, check_tol (see
pymor.core.defaults)
-
pymor.algorithms.gram_schmidt.gram_schmidt_biorth(V, W, product=None, reiterate=True, reiteration_threshold=0.1, check=True, check_tol=0.001, copy=True)[source]¶ Biorthonormalize a pair of
VectorArraysusing the biorthonormal Gram-Schmidt process.See Algorithm 1 in [BKS11].
[BKS11] P. Benner, M. Köhler, J. Saak, Sparse-Dense Sylvester Equations in 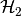 -Model Order Reduction,
Max Planck Institute Magdeburg Preprint, available from http://www.mpi-magdeburg.mpg.de/preprints/,
2011.
-Model Order Reduction,
Max Planck Institute Magdeburg Preprint, available from http://www.mpi-magdeburg.mpg.de/preprints/,
2011.Parameters
- V, W
- The
VectorArrayswhich are to be biorthonormalized. - product
- The inner product
Operatorw.r.t. which to biorthonormalize. IfNone, the Euclidean product is used. - reiterate
- If
True, orthonormalize again if the norm of the orthogonalized vector is much smaller than the norm of the original vector. - reiteration_threshold
- If
reiterateisTrue, re-orthonormalize if the ratio between the norms of the orthogonalized vector and the original vector is smaller than this value. - check
- If
True, check if the resultingVectorArrayis really orthonormal. - check_tol
- Tolerance for the check.
- copy
- If
True, create a copy ofVandWinstead of modifyingVandWin-place.
Returns
The biorthonormalized
VectorArrays.
greedy module¶
-
pymor.algorithms.greedy.greedy(discretization, reductor, samples, use_estimator=True, error_norm=None, atol=None, rtol=None, max_extensions=None, extension_params=None, pool=None)[source]¶ Greedy basis generation algorithm.
This algorithm generates a reduced basis by iteratively adding the worst approximated solution snapshot for a given training set to the reduced basis. The approximation error is computed either by directly comparing the reduced solution to the detailed solution or by using an error estimator (
use_estimator == True). The reduction and basis extension steps are performed by calling the methods provided by thereductorandextension_algorithmarguments.Parameters
- discretization
- The
Discretizationto reduce. - reductor
- Reductor for reducing the given
Discretization. This has to be a an object with areducemethod, such thatreductor.reduce()yields the reduced discretization, and anexted_basismethod, such thatreductor.extend_basis(U, copy_U=False, **extension_params)extends the current reduced basis by the vectors contained inU. For an example seeCoerciveRBReductor. - samples
- The set of
Parametersamples on which to perform the greedy search. - use_estimator
- If
True, usereduced_discretization.estimate()to estimate the errors on the sample set. Otherwisediscretization.solve()is called to compute the exact model reduction error. - error_norm
- If
use_estimator == False, use this function to calculate the norm of the error. IfNone, the Euclidean norm is used. - atol
- If not
None, stop the algorithm if the maximum (estimated) error on the sample set drops below this value. - rtol
- If not
None, stop the algorithm if the maximum (estimated) relative error on the sample set drops below this value. - max_extensions
- If not
None, stop the algorithm aftermax_extensionsextension steps. - extension_params
dictof parameters passed to thereductor.extend_basismethod.- pool
- If not
None, theWorkerPoolto use for parallelization.
Returns
Dict with the following fields
reduced_discretization: The reduced Discretizationobtained for the computed basis.max_errs: Sequence of maximum errors during the greedy run. max_err_mus: The parameters corresponding to max_errs.extensions: Number of performed basis extensions. time: Total runtime of the algorithm. reduction_data: The reduction_datareturned by the lastreductorcall.
image module¶
-
class
pymor.algorithms.image.CollectOperatorRangeRules[source]¶ Bases:
pymor.algorithms.rules.RuleTableRuleTablefor theestimate_imagealgorithm.Methods
RuleTableappend_rule,apply,apply_children,get_children,insert_rule,replace_childrenBasicInterfacedisable_logging,enable_logging,has_interface_name,implementor_names,implementorsAttributes
CollectOperatorRangeRulesaction_apply_operator,action_Concatenation,action_EmpiricalInterpolatedOperator,action_recurse,rulesBasicInterfacelogger,logging_disabled,name,uid
-
class
pymor.algorithms.image.CollectVectorRangeRules[source]¶ Bases:
pymor.algorithms.rules.RuleTableRuleTablefor theestimate_imagealgorithm.Methods
RuleTableappend_rule,apply,apply_children,get_children,insert_rule,replace_childrenBasicInterfacedisable_logging,enable_logging,has_interface_name,implementor_names,implementorsAttributes
CollectVectorRangeRulesaction_as_range_array,action_recurse,action_VectorArray,rulesBasicInterfacelogger,logging_disabled,name,uid
-
pymor.algorithms.image.estimate_image(operators=(), vectors=(), domain=None, extends=False, orthonormalize=True, product=None, riesz_representatives=False)[source]¶ Estimate the image of given
Operatorsfor all mu.Let
operatorsbe a list ofOperatorswith common source and range, and letvectorsbe a list ofVectorArraysor vector-likeOperatorsin the range of these operators. Given aVectorArraydomainof vectors in the source of the operators, this algorithms determines aVectorArrayimageof range vectors such that the linear span ofimagecontains:op.apply(U, mu=mu)for all operatorsopinoperators, for all possibleParametersmuand for allVectorArraysUcontained in the linear span ofdomain,Ufor allVectorArraysinvectors,v.as_range_array(mu)for allOperatorsinvectorsand all possibleParametersmu.
The algorithm will try to choose
imageas small as possible. However, no optimality is guaranteed. The image estimation algorithm is specified byCollectOperatorRangeRulesandCollectVectorRangeRules.Parameters
- operators
- See above.
- vectors
- See above.
- domain
- See above. If
None, an emptydomainVectorArrayis assumed. - extends
- For some operators, e.g.
EmpiricalInterpolatedOperator, as well as for all elements ofvectors,imageis estimated independently from the choice ofdomain. IfextendsisTrue, such operators are ignored. (This is useful in case these vectors have already been obtained by earlier calls to this function.) - orthonormalize
- Compute an orthonormal basis for the linear span of
imageusing thegram_schmidtalgorithm. - product
- Inner product
Operatorw.r.t. which to orthonormalize. - riesz_representatives
- If
True, compute Riesz representatives of the vectors inimagebefore orthonormalizing (useful for dual norm computation when the range of theoperatorsis a dual space).
Returns
The
VectorArrayimage.Raises
- ImageCollectionError
- Is raised when for a given
Operatorno image estimate is possible.
-
pymor.algorithms.image.estimate_image_hierarchical(operators=(), vectors=(), domain=None, extends=None, orthonormalize=True, product=None, riesz_representatives=False)[source]¶ Estimate the image of given
Operatorsfor all mu.This is an extended version of
estimate_image, which callsestimate_imageindividually for each vector ofdomain.As a result, the vectors in the returned
imageVectorArraywill be ordered by thedomainvector they correspond to (starting with vectors which correspond to thefunctionalsand toOperatorsfor which the image is estimated independently fromdomain).This function also returns an
image_dimslist, such that the firstimage_dims[i+1]vectors ofimagecorrespond to the firstivectors ofdomain(the firstimage_dims[0]vectors correspond tovectorsand toOperatorswith fixed image estimate).Parameters
- operators
- See
estimate_image. - vectors
- See
estimate_image. - domain
- See
estimate_image. - extends
- When additional vectors have been appended to the
domainVectorArrayafterestimate_image_hierarchicalhas been called, andestimate_image_hierarchicalshall be called again for the extendeddomainarray,extendscan be set to(image, image_dims), whereimage,image_dimsare the return values of the lastestimate_image_hierarchicalcall. The olddomainvectors will then be skipped during computation andimage,image_dimswill be modified in-place. - orthonormalize
- See
estimate_image. - product
- See
estimate_image. - riesz_representatives
- See
estimate_image.
Returns
- image
- See above.
- image_dims
- See above.
Raises
- ImageCollectionError
- Is raised when for a given
Operatorno image estimate is possible.
newton module¶
-
pymor.algorithms.newton.newton(operator, rhs, initial_guess=None, mu=None, error_norm=None, least_squares=False, miniter=0, maxiter=100, rtol=-1.0, atol=-1.0, stagnation_window=3, stagnation_threshold=0.9, return_stages=False, return_residuals=False)[source]¶ Basic Newton algorithm.
This method solves the nonlinear equation
A(U, mu) = V
for
Uusing the Newton method.Parameters
- operator
- The
OperatorA.Amust implement thejacobianinterface method. - rhs
VectorArrayof length 1 containing the vectorV.- initial_guess
- If
None, aVectorArrayof length 1 containing an initial guess for the solutionU. - mu
- The
Parameterfor which to solve the equation. - error_norm
- The norm with which the norm of the residual is computed. If
None, the Euclidean norm is used. - least_squares
- If
True, use a least squares linear solver (e.g. for residual minimization). - miniter
- Minimum amount of iterations to perform.
- maxiter
- Fail if the iteration count reaches this value without converging.
- rtol
- Finish when the residual norm has been reduced by this factor relative to the norm of the initial residual.
- atol
- Finish when the residual norm is below this threshold.
- stagnation_window
- Finish when the residual norm has not been reduced by a factor of
stagnation_thresholdduring the laststagnation_windowiterations. - stagnation_threshold
- See
stagnation_window. - return_stages
- If
True, return aVectorArrayof the intermediate approximations ofUafter each iteration. - return_residuals
- If
True, return aVectorArrayof all residual vectors which have been computed during the Newton iterations.
Returns
- U
VectorArrayof length 1 containing the computed solution- data
Dict containing the following fields:
error_sequence: NumPy arraycontaining the residual norms after each iteration.stages: See return_stages.residuals: See return_residuals.
Raises
- NewtonError
- Raised if the Netwon algorithm failed to converge.
Defaults
miniter, maxiter, rtol, atol, stagnation_window, stagnation_threshold (see
pymor.core.defaults)
pod module¶
-
pymor.algorithms.pod.pod(A, modes=None, product=None, rtol=4e-08, atol=0.0, l2_err=0.0, symmetrize=False, orthonormalize=True, check=True, check_tol=1e-10)[source]¶ Proper orthogonal decomposition of
A.Viewing the
VectorArrayAas aA.dimxlen(A)matrix, the return value of this method is theVectorArrayof left-singular vectors of the singular value decomposition ofA, where the inner product on R^(dim(A)) is given byproductand the inner product on R^(len(A)) is the Euclidean inner product.Parameters
- A
- The
VectorArrayfor which the POD is to be computed. - modes
- If not
None, only the firstmodesPOD modes (singular vectors) are returned. - product
- Inner product
Operatorw.r.t. which the POD is computed. - rtol
- Singular values smaller than this value multiplied by the largest singular value are ignored.
- atol
- Singular values smaller than this value are ignored.
- l2_err
Do not return more modes than needed to bound the l2-approximation error by this value. I.e. the number of returned modes is at most
argmin_N { sum_{n=N+1}^{infty} s_n^2 <= l2_err^2 }
where
s_ndenotes the n-th singular value.- symmetrize
- If
True, symmetrize the Gramian again before proceeding. - orthonormalize
- If
True, orthonormalize the computed POD modes again using thegram_schmidtalgorithm. - check
- If
True, check the computed POD modes for orthonormality. - check_tol
- Tolerance for the orthonormality check.
Returns
- POD
VectorArrayof POD modes.- SVALS
- Sequence of singular values.
Defaults
rtol, atol, l2_err, symmetrize, orthonormalize, check, check_tol (see
pymor.core.defaults)
preassemble module¶
-
class
pymor.algorithms.preassemble.PreAssembleRules[source]¶ Bases:
pymor.algorithms.rules.RuleTableMethods
RuleTableappend_rule,apply,apply_children,get_children,insert_rule,replace_childrenBasicInterfacedisable_logging,enable_logging,has_interface_name,implementor_names,implementorsAttributes
PreAssembleRulesaction_AdjointOperator,action_assemble,action_identity,action_recurse,action_recurse_and_assemble,rulesBasicInterfacelogger,logging_disabled,name,uid
projection module¶
-
class
pymor.algorithms.projection.ProjectRules[source]¶ Bases:
pymor.algorithms.rules.RuleTableRuleTablefor theprojectalgorithm.Methods
RuleTableappend_rule,apply,apply_children,get_children,insert_rule,replace_childrenBasicInterfacedisable_logging,enable_logging,has_interface_name,implementor_names,implementorsAttributes
ProjectRulesaction_AdjointOperator,action_AffineOperator,action_apply_basis,action_Concatenation,action_ConstantOperator,action_EmpiricalInterpolatedOperator,action_generic_projection,action_recurse,action_ZeroOperator,rulesBasicInterfacelogger,logging_disabled,name,uid
-
class
pymor.algorithms.projection.ProjectToSubbasisRules[source]¶ Bases:
pymor.algorithms.rules.RuleTableRuleTablefor theproject_to_subbasisalgorithm.Methods
RuleTableappend_rule,apply,apply_children,get_children,insert_rule,replace_childrenBasicInterfacedisable_logging,enable_logging,has_interface_name,implementor_names,implementorsAttributes
ProjectToSubbasisRulesaction_ConstantOperator,action_NumpyMatrixOperator,action_ProjectedEmpiciralInterpolatedOperator,action_ProjectedOperator,action_recurse,rulesBasicInterfacelogger,logging_disabled,name,uid
-
pymor.algorithms.projection.project(op, range_basis, source_basis, product=None)[source]¶ Petrov-Galerkin projection of a given
Operator.Given an inner product
( ⋅, ⋅), source vectorsb_1, ..., b_Nand range vectorsc_1, ..., c_M, the projectionop_projofopis defined by[ op_proj(e_j) ]_i = ( c_i, op(b_j) )
for all i,j, where
e_jdenotes the j-th canonical basis vector of R^N.In particular, if the
c_iare orthonormal w.r.t. the given product, thenop_projis the coordinate representation w.r.t. theb_i/c_ibases of the restriction ofoptospan(b_i)concatenated with the orthogonal projection ontospan(c_i).From another point of view, if
opis viewed as a bilinear form (seeapply2) and( ⋅, ⋅ )is the Euclidean inner product, thenop_projrepresents the matrix of the bilinear form restricted tospan(b_i) / span(c_i)(w.r.t. theb_i/c_ibases).How the projection is realized will depend on the given
Operator. While a projectedNumpyMatrixOperatorwill again be aNumpyMatrixOperator, only a genericProjectedOperatorcan be returned in general. The exact algorithm is specified inProjectRules.Parameters
- range_basis
- The vectors
c_1, ..., c_Mas aVectorArray. IfNone, no projection in the range space is performed. - source_basis
- The vectors
b_1, ..., b_Nas aVectorArrayorNone. IfNone, no restriction of the source space is performed. - product
- An
Operatorrepresenting the inner product. IfNone, the Euclidean inner product is chosen.
Returns
The projected
Operatorop_proj.
-
pymor.algorithms.projection.project_to_subbasis(op, dim_range=None, dim_source=None)[source]¶ Project given already projected
Operatorto a subbasis.The purpose of this method is to further project an operator that has been obtained through
projectto subbases of the original projection bases, i.e.project_to_subbasis(project(op, r_basis, s_basis, prod), dim_range, dim_source)
should be the same as
project(op, r_basis[:dim_range], s_basis[:dim_source], prod)
For a
NumpyMatrixOperatorthis amounts to extracting the upper-left (dim_range, dim_source) corner of its matrix.The subbasis projection algorithm is specified in
ProjectToSubbasisRules.Parameters
- dim_range
- Dimension of the range subbasis.
- dim_source
- Dimension of the source subbasis.
Returns
The projected
Operator.
rules module¶
-
class
pymor.algorithms.rules.RuleTable[source]¶ Bases:
pymor.core.interfaces.BasicInterfaceDefine algorithm by a table of match conditions and corresponding actions.
RuleTablemanages a table ofrules, stored in therulesattributes, which can beappliedto given objects.A new table is created by subclassing
RuleTableand defining new methods which are decorated withmatch_class,match_genericor anotherrulesubclass. The order of the method definitions determines the order in which the definedrulesare applied.Methods
RuleTableappend_rule,apply,apply_children,get_children,insert_rule,replace_childrenBasicInterfacedisable_logging,enable_logging,has_interface_name,implementor_names,implementorsAttributes
RuleTablerulesBasicInterfacelogger,logging_disabled,name,uid-
apply(obj, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Sequentially apply rules to given object.
This method iterates over all rules of the given
RuleTable. For eachrule, it is checked if itmatchesthe given object. IfFalse, the nextrulein the table is considered. IfTruethe correspondingactionis executed withobj,*argsand**kwargsas parameters. If execution ofactionraisesRuleNotMatchingError, the rule is considered as not matching, and execution continues with evaluation of the next rule. Otherwise, execution is stopped and the return value ofrule.actionis returned to the caller.If no
rulematches, aNoMatchingRuleErroris raised.Parameters
Returns
Return value of the action of the first matching
rulein the table.Raises
- NoMatchingRuleError
- No
rulecould be applied to the given object.
-
apply_children(obj, *args, *, children=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Apply rules to all children of the given object.
This method calls
applyto each child of the given object. The children of the object are either provided by thechildrenparameter or authomatically infered by theget_childrenmethod.Parameters
Returns
Result of : meth:
applyfor all given children.
-
classmethod
get_children(obj)[source]¶ Determine children of given object.
This method returns a list of the names of all attributes
a, for which one of the folling is true:
-
replace_children(obj, *args, *, children=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Replace children of object according to rule table.
Same as
apply_children, but additionally callsobj.with_to replace the children ofobjwith the result of the correspondingapplycall.
-
-
class
pymor.algorithms.rules.RuleTableMeta(name, bases, namespace)[source]¶ Bases:
pymor.core.interfaces.UberMetaMeta class for
RuleTable.
-
class
pymor.algorithms.rules.match_class(*classes)[source]¶ Bases:
pymor.algorithms.rules.rulerulethat matches when obj is instance of one of the given classes.Methods
match_classmatchesAttributes
match_classcondition_typeruleaction,action_description,condition_description,source
-
class
pymor.algorithms.rules.match_generic(condition, condition_description=None)[source]¶ Bases:
pymor.algorithms.rules.rulerulewith matching condition given by an arbitrary function.Parameters
- condition
- Function of one argument which checks if given object matches condition.
- condition_description
- Optional string describing the condition implemented by
condition.
Methods
match_genericmatchesAttributes
match_genericcondition_typeruleaction,action_description,condition_description,source
-
class
pymor.algorithms.rules.rule[source]¶ Bases:
objectDecorator to make a method a rule in a given
RuleTable.The decorated function will become the
actionto perform in case the rulematches. Matching conditions are specified by subclassing and overriding thematchesmethod.-
action¶ Method to call in case the rule matches.
-
timestepping module¶
This module provides generic time-stepping algorithms for the solution of instationary problems.
The algorithms are generic in the sense that each algorithms operates exclusively
on Operators and VectorArrays. In particular, the algorithms
can also be used to turn an arbitrary stationary Discretization provided
by an external library into an instationary Discretization.
Currently, implementations of explicit_euler and implicit_euler
time-stepping are provided. The TimeStepperInterface defines a
common interface that has to be fulfilled by the time-steppers used
by InstationaryDiscretization. The classes ExplicitEulerTimeStepper
and ImplicitEulerTimeStepper encapsulate explicit_euler and
implicit_euler to provide this interface.
-
class
pymor.algorithms.timestepping.ExplicitEulerTimeStepper(nt)[source]¶ Bases:
pymor.algorithms.timestepping.TimeStepperInterfaceExplicit Euler time-stepper.
Solves equations of the form
M * d_t u + A(u, mu, t) = F(mu, t).
Parameters
- nt
- The number of time-steps the time-stepper will perform.
-
class
pymor.algorithms.timestepping.ImplicitEulerTimeStepper(nt, solver_options='operator')[source]¶ Bases:
pymor.algorithms.timestepping.TimeStepperInterfaceImplict Euler time-stepper.
Solves equations of the form
M * d_t u + A(u, mu, t) = F(mu, t).
Parameters
- nt
- The number of time-steps the time-stepper will perform.
- solver_options
- The
solver_optionsused to invertM + dt*A. The special values'mass'and'operator'are recognized, in which case the solver_options of M (resp. A) are used.
-
class
pymor.algorithms.timestepping.TimeStepperInterface[source]¶ Bases:
pymor.core.interfaces.ImmutableInterfaceInterface for time-stepping algorithms.
Algorithms implementing this interface solve time-dependent problems of the form
M * d_t u + A(u, mu, t) = F(mu, t).
Time-steppers used by
InstationaryDiscretizationhave to fulfill this interface.Methods
TimeStepperInterfacesolveImmutableInterfacegenerate_sid,with_,__setattr__BasicInterfacedisable_logging,enable_logging,has_interface_name,implementor_names,implementorsAttributes
ImmutableInterfaceadd_with_arguments,sid,sid_ignore,with_argumentsBasicInterfacelogger,logging_disabled,name,uid-
solve(initial_time, end_time, initial_data, operator, rhs=None, mass=None, mu=None, num_values=None)[source]¶ Apply time-stepper to the equation
M * d_t u + A(u, mu, t) = F(mu, t).
Parameters
- initial_time
- The time at which to begin time-stepping.
- end_time
- The time until which to perform time-stepping.
- initial_data
- The solution vector at
initial_time. - operator
- The
OperatorA. - rhs
- The right-hand side F (either
VectorArrayof length 1 orOperatorwithrange.dim == 1). IfNone, zero right-hand side is assumed. - mass
- The
OperatorM. IfNone, the identity operator is assumed. - mu
Parameterfor whichoperatorandrhsare evaluated. The current time is added tomuwith key_t.- num_values
- The number of returned vectors of the solution trajectory. If
None, each intermediate vector that is calculated is returned.
Returns
VectorArraycontaining the solution trajectory.
-
-
pymor.algorithms.timestepping.explicit_euler(A, F, U0, t0, t1, nt, mu=None, num_values=None)[source]¶
to_matrix module¶
-
class
pymor.algorithms.to_matrix.ToMatrixRules[source]¶ Bases:
pymor.algorithms.rules.RuleTableMethods
RuleTableappend_rule,apply,apply_children,get_children,insert_rule,replace_childrenBasicInterfacedisable_logging,enable_logging,has_interface_name,implementor_names,implementorsAttributes
ToMatrixRulesaction_AdjointOperator,action_BlockOperator,action_ComponentProjection,action_Concatenation,action_IdentityOperator,action_LincombOperator,action_NumpyMatrixOperator,action_VectorArrayOperator,action_ZeroOperator,rulesBasicInterfacelogger,logging_disabled,name,uid
-
pymor.algorithms.to_matrix.to_matrix(op, format=None, mu=None)[source]¶ Transfrom construction of NumpyMatrixOperators to NumPy or SciPy array
Parameters
- op
- Operator.
- format
- Format of the resulting
SciPy spmatrix. IfNone, a dense format is used. - mu
Parameter.
Returns
- res
- Equivalent matrix.