The BESIII experiment
The BESIII-Experiment (BEijing Spectrometer) is an internal experiment at the accelerator complex BEPC-II (Beijing Electron Positron Collider) at the institute for high energy physics (IHEP) in Beijing. Electrons and positrons are accelerated in two distinct storage rings before being brought to collision at center-of-mass energies between 2.0 and 4.9 GeV.
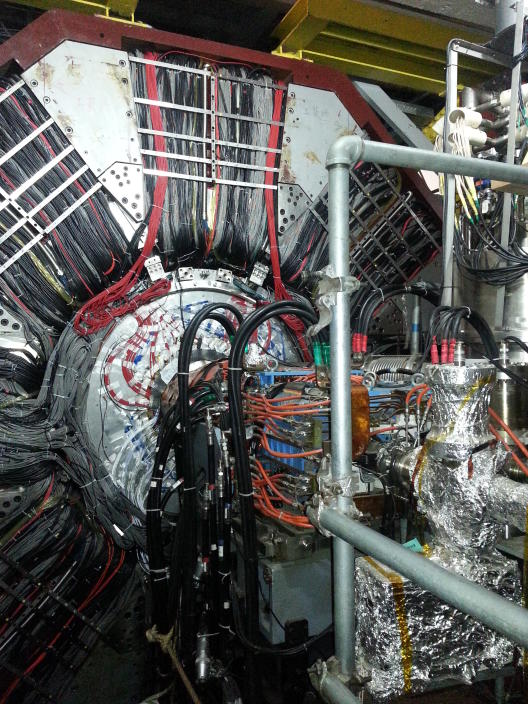
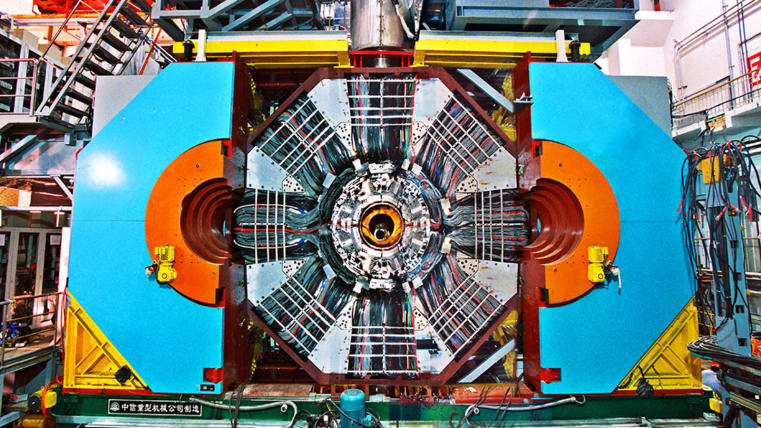

The BESIII-Spectrometer is built right around the interaction point. Within its shell-like structure, a drift chamber, time-of-flight detector, electromagnetic calorimeter and a muon detector are used to reconstruct final state particles.
One of the main objectives of the BESIII-Experiment is the investigation of the charmonium spectrum. Mesons (qq̅ pairs) are denoted as charmonium when they are built up by a charm anti-charm (cc̅ ) quark pair. A prominent example for such a charmonium is the JPC=1-- J/ψ. Its discovery in the year 1974 at the same time meant the discovery of the charm quark itself. Ever since this first detection numerous other states were found and successfully classified into the charmonium spectrum.
Apart from the aforementioned mesons (qq̅ ) and the baryons (qqq), the strong interaction also allows more exotic systems consisting of four quarks (tetraquarks or molecules), five quarks (pentaquarks), a mixture of quarks and gluons (hybrids) and glueballs, consisting entirely of gluons.
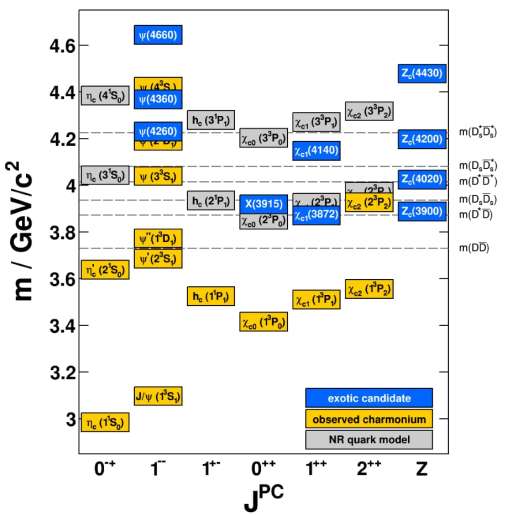
Over the years, many more states were discovered than originally predicted for the spectrum of conventional (cc̅ ) charmonium. Thus, these supernumerous states need to be regarded as exotic particles. The BESIII-Experiment is one of the leading experiments in the search for such exotic states and in the attempt to resolve their nature.
Within our working group a wide spectrum of analyses is performed. Apart from the analysis of final states containing a proton-antiproton pair and an additional particle like the π, η or ω-meson, another focus lies in the production of light hadrons and the investigation of possible couplings of them to exotic states like the Y(4260) and the X(1835). Another focus lies in the analysis of ηc decays which also play role in the search for exotic states. In addition, these analyses contribute to the search for glueballs. The Partial Wave Analysis is one of the modern commonly used data analysis techniques to perform such analyses.
