Solitons:
Particle-like structures in self-organized systems
Solitons are classical waves that behaves like particles. They can be observed as electromagnetic pulses in electrical and optical transmission lines, as large water waves (tsunami), as current-filaments in plasma systems, and as nerve pulses. There are conservative solitons (the only really nonlinear objects that we can handle) and dissipative solitons. We are going to discuss the following problems:
 |
 |
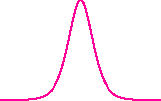
| Classical soliton |
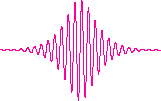
Envelope soliton |
| |
 |
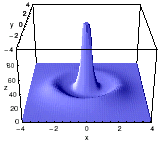 |
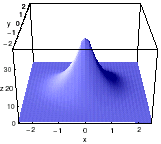
| Two examples from the experiment: dissipative solitons |
- Wave concept in physics: linear waves, phase velocity and group velocity, dispersion effect
- Nonlinearity and waves: stationary waves and pulse solutions, shocks, burgers equation
- Waves on shallow water: Korteweg-de Vries equation, basic solutions and observations
- Modulation instability and envelope solitons: nonlinear Schrödinger equation
- Effect of wave interaction: experiments on deep water, modulation effect for electromagnetic waves
- Experimental investigation of nonlinear waves: electrical networks, solitons and kinks
- Particle properties of solitons: mathematical technique, inverse scattering
- Solitons in two and three dimensions: collapse, dissipative solitons and self-organization
- Applications.





